Guide Description
Despite Western media's assimilated perception of what constitutes "African" culture, Africa is a continent recognized for its vast ethnolinguistic diversity. Home to over 2,000 spoken languages and numerous tribes, Africa makes up approximately one third of the world's languages.
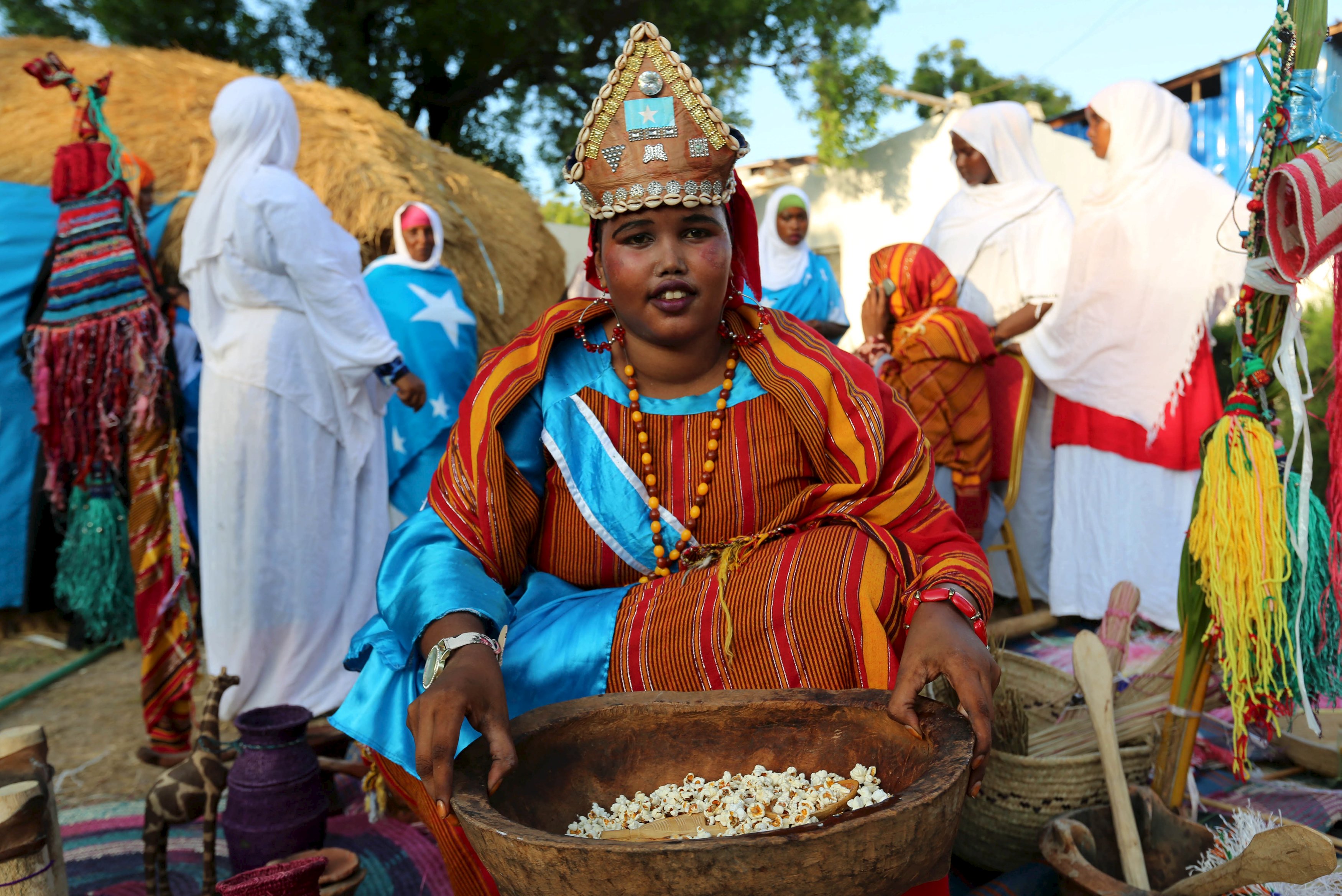
Somali woman dressed in traditional attire
Although there's no way to record all the minority/endangered languages, this guide aims to provide extensive information on recorded languages of Africa for those interested in exploring the continent's linguistic diversity and history using a variety of sources.
The guide also focuses primarily on African indigenous languages, excluding colonial languages such as English, French, etc.
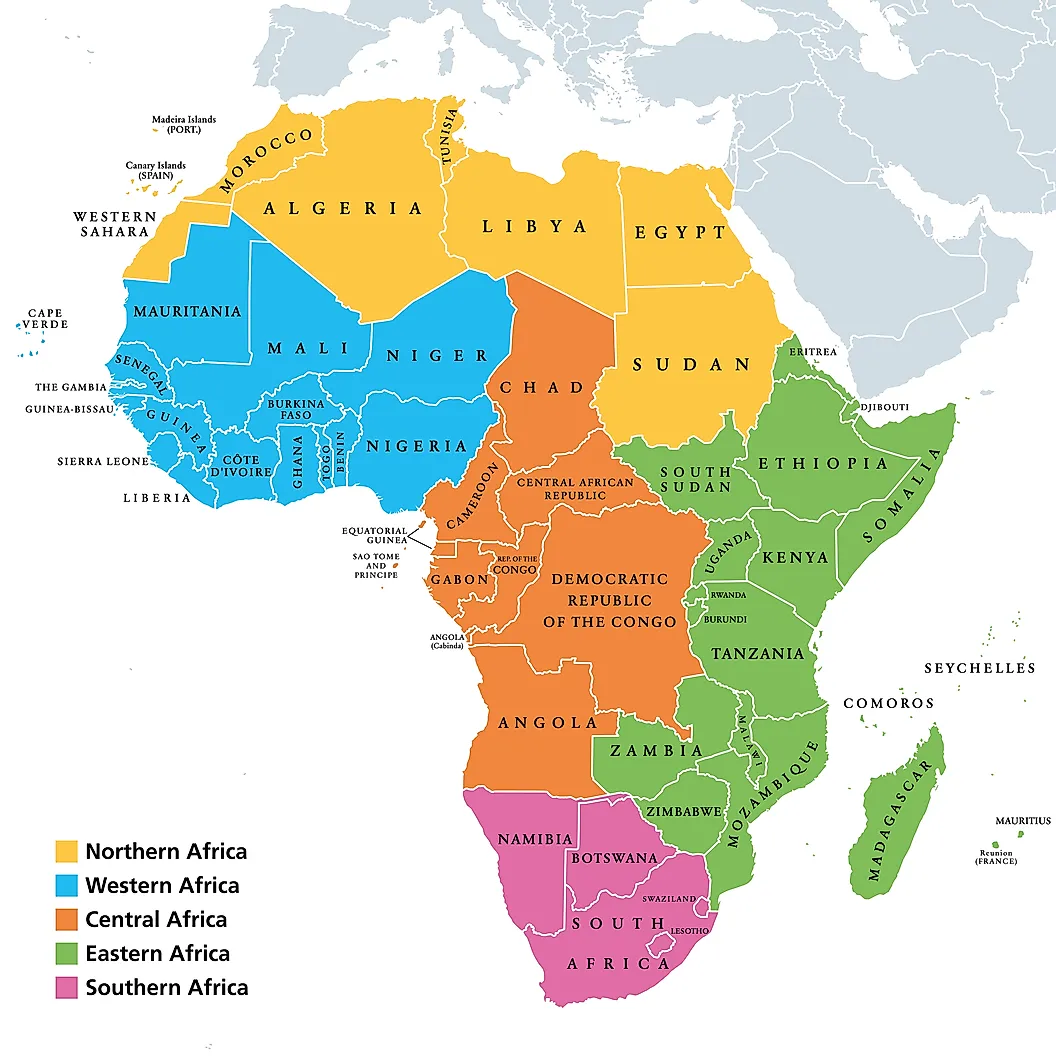
Map of Africa
This guide groups Africa's countries and their respective languages by region: Northern Africa, Western Africa, Central Africa, Eastern Africa and Southern Africa. Asides geographical comparability pertaining to climate and location, most countries within their respective regions tend to share cultural similarities.
There are various countries within each region:
Northern Africa
Countries within the region of North Africa include Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Sudan and Tunisia.
West Africa
Countries within the region of West Africa include Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone and Togo.
Central Africa
Countries within the region of Central Africa include Angola, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon and São Tomé and Príncipe.
East Africa
Countries within the region of East Africa include Burundi, Comoros, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Mozambique, Rwanda, Seychelles, Somalia, South Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
Southern Africa
Countries within the region of Southern Africa include Botswana, Eswatini (Swaziland), Lesotho, Namibia and South Africa.
Kodjo Atiso - Librarian
African Language Families
Africa's many languages can be classified into categories known as language families, which is a grouping system utilized based on their common descent from an ancestral language.
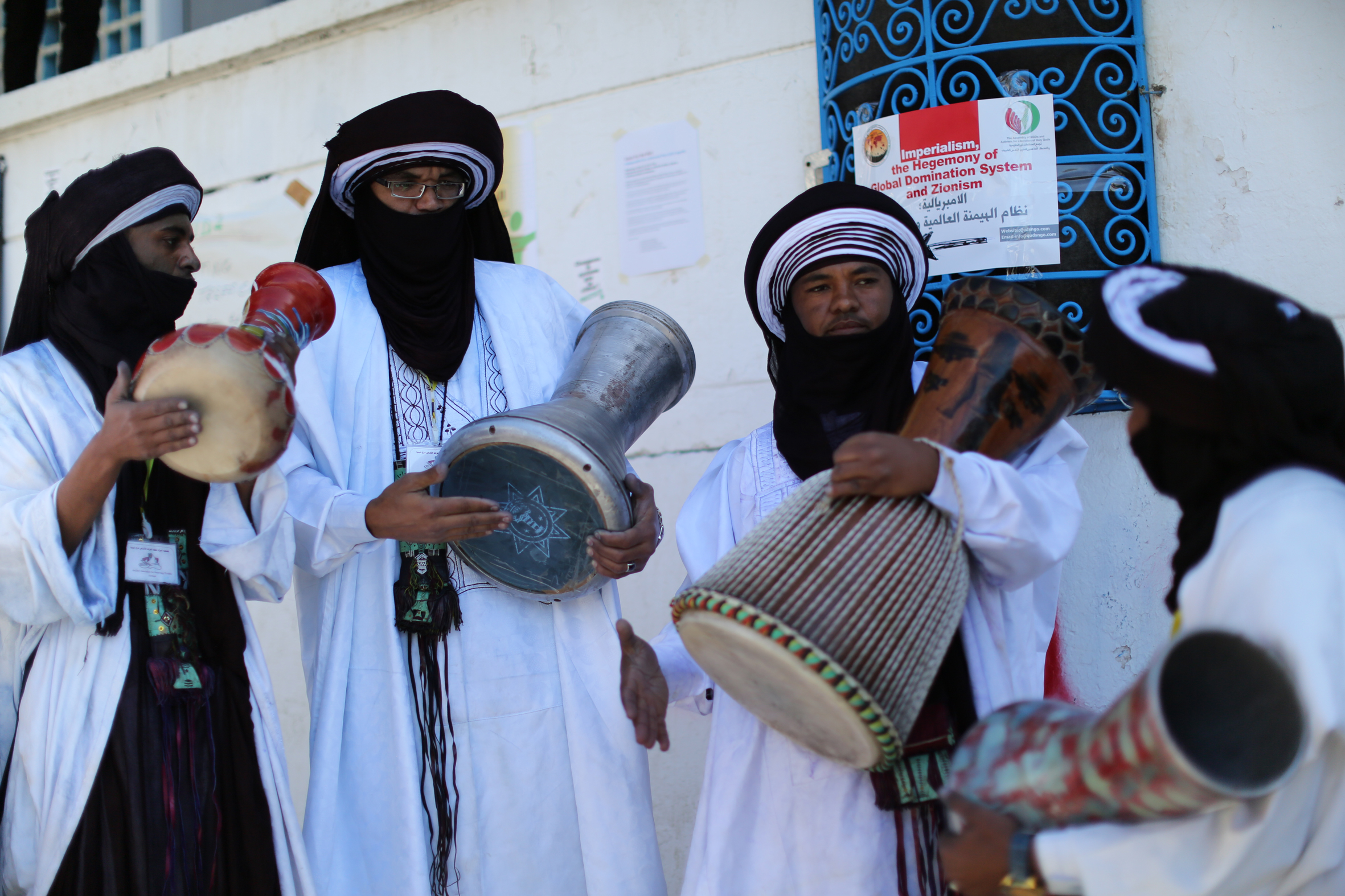
Tunisian participants in the 14th World Social Forum
Excluding the Austronesian (Malayo-Polynesian) family of languages represented in Madagascar, there are four major African language families represented in the continent:
Afro-Asiatic Language Family
This language family consists of 200-300 languages, making it the second largest language family of the four. Afro-Asiatic languages are primarily found in North Africa and Northern regions of other countries.
Niger-Congo Language Family
In addition to constituting the most widely spoken languages in Africa, the Niger-Congo language family is comprised from 1,350-1,650 languages, establishing its position as the largest language family in the world. Niger-Congo languages are allocated to various African regions, inhabiting Western, Central, Eastern and Southern Africa.
Nilo-Saharan Language Family
There are about 80 languages found within the Nilo-Saharan language family. These languages are primarily found in East Africa and Northeastern regions.
Khoisan Language Family
The Khoisan language family is the smallest of the four. Primarily found in Southern Africa, there are 40-70 languages that constitute this language family.